ARRYTHMOGENIC RIGHT VENTRICULAR DYSPLASIA
Notes
· Use Anterior Surface Coil only & turn off the posterior coil to avoid wraparound artifact
· Consider prone positioning for obese patients
· Make sure the entire right ventricle is included on all scans.
· Use SENSE to improve imaging time.
· Slice thickness 6 - 8 mm, with 2 - 4 mm interslice gaps to equal 10 mm (unless otherwise indicated)
Pulse Sequences
1. 3 Plane Survey
1. B-TFE (Axial) (8 - 10 mm slice thickness)
2.
INTERACTIVE
3. T1_TSE-BB (4 Chamber) *Include RVOT
4. T1_TSE-BB FS(4 Chamber) *Include RVOT
5. T1_TSE-BB (Short Axis)
6. T2W-BB (4 Chamber)
7.
DYNAMIC FIRST-PASS PERFUSION
8. B-TFE_BH (4 Chamber)
9. B-TFE_BH (RVOT)
10. B-TFE_BH (Short Axis) *This series is used for ejection fraction calculation and should be relatively motion free.
11.
IR_TFE_LOOKLOCKER *(make sure right ventricle
myocardium is nulled; RV inversion time may be up to 50 ms less than LV)
12. IR_TFE_3D_BH (4 Chamber)
13. IR_TFE_3D_BH (Short Axis)
14. IR_TFE_3D_BH (2 Chamber)
15. IR_TFE_3D_BH (RV 2 Chamber)
References & Illustrations
Ø Arrhythmogenic Right Ventricular Dysplasia http://www.aafp.org/afp/2006/0415/p1391.html
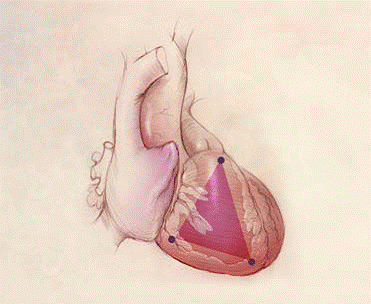
o The most common location for this tissue transformation is between the anterior infundibulum, right ventricular apex, and inferior or diaphragmatic aspect of the right ventricle, the so-called “triangle of dysplasia” as indicated below…
Ø
Standardized cardiovascular magnetic resonance
imaging (CMR) protocols, society for cardiovascular magnetic resonance: board
of trustees task force on standardized protocols http://scmr.org/assets/files/1532-429X-10-35.pdf
Phase Contrast Articles
Ø Cardiovascular Applications of Phase-Contrast MRI http://www.ajronline.org/cgi/content/full/192/3/662
Ø Cardiovascular Flow Measurement with Phase-Contrast MR Imaging: Basic Facts and Implementation http://radiographics.rsna.org/content/22/3/651.full
SVC and Inferior Vena Cava:
The encoding velocity for the first measurement or for
flow measurement is 110
cm/sec. The usual velocity for peak velocity measurement is 50–80 cm/sec.
Ascending Aorta:
The encoding velocity for the first measurement or
for flow measurement is 200 cm/sec. The usual velocity for peak velocity measurement is 100–160 cm/sec.
Main Pulmonary Artery:
The encoding velocity for the first measurement or
for flow measurement is 180 cm/sec. The usual velocity for peak velocity measurement is 60–120 cm/sec.
Right and Left Pulmonary Arteries:
The encoding velocity for the first measurement or
for flow measurement is 200 cm/sec. The usual velocity for peak velocity measurement is 60–120 cm/sec.
Ø Quantification of Flow Dynamics in
Congenital Heart Disease: Applications of Velocity-encoded Cine MR Imaging http://radiographics.rsna.org/content/22/4/895.full
Rev: 5/13/10